4-3, Ten Hour, Rotating Shift Pattern| 24/7 Shift Coverage
The 4-3 Ten Hour Rotating Shift schedule uses 6 teams (crews) and 3 overlapping ten-hour shifts to provide 24/7 coverage. It consists of a 3-week cycle where each team works four consecutive 10-hour first shifts, followed by 3 days off duty, works four consecutive 10-hour third shifts, followed by 3 days off duty, works four consecutive 10-hour second shifts, followed by 3 days off duty. The overlapping shifts provide extra manpower during high activity periods. This plan requires 6 teams (a minimum of 6 employees) with 3 teams on duty and 3 teams off duty at any given day. Employees in all six teams are scheduled to work on the same day, one day a week. This day can be manipulated to fall on any day of the week to cover high activity day or in-service training. Personnel work 40 hours per week.
When emergencies arise and an employee needs to take a few days off, it can be a challenge finding a replacement to ensure adequate shift coverage while taking into consideration time-off constraints, union, labor and overtime rules, employee availability, skills, preferences, etc. Snap Schedule 365 employee scheduling software solves these challenges and help companies build smarter schedules, avoid unnecessary overtime, and always know who is working where and when. Get your free trial now.
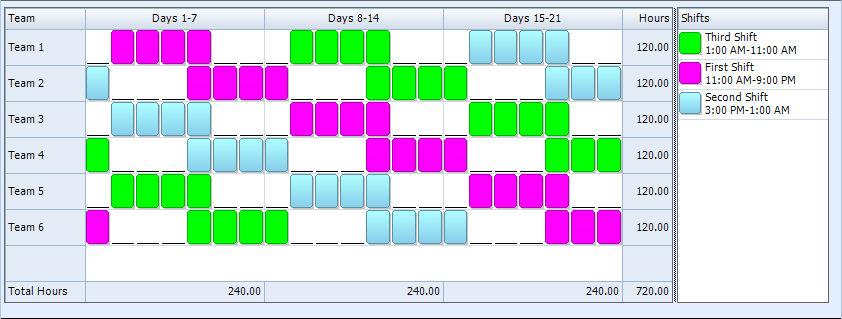
Notes:
The above grid shows working and non-working days for each team in one repeat cycle. Day 1 usually starts on a Monday but it can be any day of the week. At the end of the cycle, the entire sequence starts over. Color coded blocks represent assigned shifts (working days) while underlines represent non-working days.- The required shifts and shift lengths are shown in the Shifts column. Shift names, start times, and end times are shown as examples only. They can be changed to match the requirements of your operation.
- The teams required by the plan are shown in the first column. The total working hours for each team over the repeat cycle are shown in the Hours column, assuming one employee per team.
- The last row, Hours, shows the hours worked by all teams in each date range block (leg), assuming one employee per team.
Characteristics |
|
| Plan ID | C6TR10-1 |
|---|---|
| Name | 4-3 Ten Hour Rotating Shift Schedule |
| Applicability | 24/7 operations |
| Teams Required | 6 |
| Shifts | 10-hr |
| Repeat Cycle | 21 days |
| Rotation | Slow rotation between shifts |
| Average Hours per Week | 40 |
| Staffing Fluctuation | Balanced from shift to shift and day to day |
| Pluses |
|
| Minuses |
|
| Common Usage | Well suited to the variable workloads confronted by police departments, law enforcement agencies, emergency medical services, EMS call centers and dispatchers |
| Notes |
|
Definitions:
- Plan ID: A code used to uniquely identify the shift plan in Snap Schedule employee scheduling software.
- Name: The name of the shift plan.
- Applicability: The type of operations this shift configuration is designed for.
- Teams Required: The number of teams (crews) required by this plan. A team may consist of one or more employees.
- Shifts: The different shifts used in this shift pattern. For each shift, only the shift description and shift length are shown. The shift start or end time can be adjusted to fit your business operations so long as the shift length stays the same.
- Repeat Cycle: The number of days required for each team to complete its assigned shift sequence in a schedule plan. At the end of each repeat cycle, the team starts the same shift sequence over again.
- Rotation: For rotating shift configurations, a team rotates from one shift to another according to a specific arrangement. In a forward rotation, the team rotates from a shift that starts earlier in the day to a shift that starts later in the day, e.g. Day to Swing to Night. In a backward rotation, the reverse is true. Many studies suggest that forward rotation is better than backward rotation since our body adjusts much better to changes in work shifts from earlier to later. The rotation speed is the speed at which the shifts are rotated. In a "fast" rotation, a team rotates from one shift to another once every few days or less. In a "slow" rotation, a team works the same shift for many days or weeks before rotating to another shift.
- Average Hours Per Week: This is the average number of hours worked by each employee per week based on the shift lengths and shift sequences for this plan.
- Staffing Fluctuation: The fluctuation in staffing level as the plan progresses from shift to shift and day to day. A shift configration is "balanced from shift to shift" if the new shift will be staffed by the same number of employees as the old shift. A shift configuration is "balanced from day to day" if each day is staffed by the same number of employees. Note that by default, each team contains the same number of employees.
- Pluses: Positive aspects of the shift configuration.
- Minuses: Negative aspects of the shift configuration.
- Common Usage: Typical users of the shift configuration.
